Breast Day Surgery
Breast Lump Excision
Breast lump excision surgery is a procedure designed to remove abnormal lumps or tumors from the breast. This surgery is typically performed for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes, allowing for a clearer understanding of the lump's nature and ruling out any malignant changes.
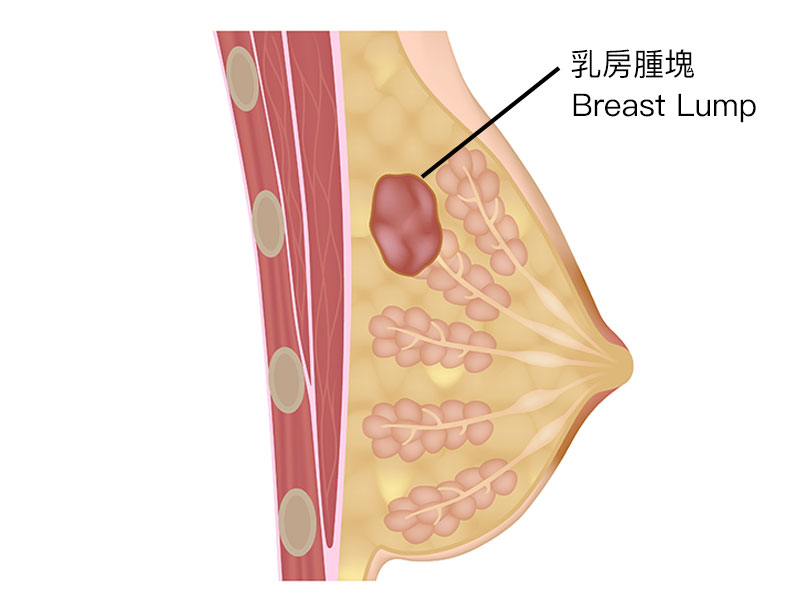
What is a Breast Lump?
A breast lump refers to the abnormal proliferation of tissue within the breast, which can be classified as either benign or malignant.
Benign lumps may include breast fibroadenomas, which are proliferations of fibrous tissue. Fibroadenomas can manifest as single or multiple lumps and may occur in one or both breasts. Generally, these lumps are asymptomatic and are often identified in women under the age of 30.
Another common type of benign lump is a breast cyst, characterized by one or several fluid-filled cysts. This condition is most prevalent among women aged 30 to 50, with studies indicating that up to 40% of women may experience this issue. Breast cysts are categorized as "simple cysts," "complex cysts," and "cystic tumors."
Simple cysts contain only fluid, with minimal to no cellular content, and are considered 100% benign. The fluid is derived from the secretion of breast tissue, and when it cannot be reabsorbed, it accumulates to form a cyst, which is encased by a thin membrane but does not become malignant.
Complex cysts and cystic tumors contain solid components alongside fluid. While these may be benign, they can also be malignant, thus requiring further tissue extraction for examination.
Malignant lumps are indicative of breast cancer.
Causes of Breast Lumps
The etiology of breast lumps is diverse, encompassing genetic mutations that lead to malignant tumors, tissue proliferation, and hormonal imbalances that result in excessive estrogen or insufficient progesterone secretion.
Women may encounter breast lumps at various life stages due to different factors. For instance, hormonal fluctuations during menstruation can result in hard lumps, swelling, or tenderness in the breasts. During pregnancy, the proliferation of milk-secreting tissue can cause swelling and a sensation of lumps. While breastfeeding, issues such as milk accumulation or nipple infections may lead to mastitis, characterized by hard lumps, fever, redness, and pain. Approaching menopause, fluctuations in hormone levels may also contribute to the development of breast lumps.
How to Differentiate Between Benign and Malignant Lumps?
It is essential to consult a physician for a comprehensive evaluation. Healthcare providers typically conduct clinical examinations, mammograms, and tissue biopsies to ascertain whether breast issues are benign or malignant.
Initially, a clinical examination will be performed to identify any abnormalities in the breast. Subsequently, the patient may require mammography and ultrasound for further assessment. If concerns arise based on these imaging results, a tissue biopsy will be conducted for analysis by a pathologist, who will examine the tissue under a microscope for abnormalities or cancer cells.
Breast Lump Excision Surgery
If diagnostic results do not definitively indicate whether a tumor is malignant, breast lump excision surgery may be advised to obtain a conclusive diagnosis.
Breast lump excision surgery is typically performed under local, general anesthesia, or monitored anesthesia. The surgeon will make an incision slightly larger than the lump, usually at the edge of the areola or above the lump, to ensure complete removal. The excised tissue will be sent to a laboratory for histopathological examination. The incision will then be closed using fine, self-dissolving sutures. The procedure usually lasts between 45 to 60 minutes.
Excision of a breast lump is considered a low-risk and safe procedure. Most side effects are mild and temporary, including discomfort associated with general anesthesia or pain medications. Post-surgery, there may be slight bruising and swelling, which typically resolve gradually.
Preparation
-
Prior to the procedure, patients should remove any makeup, nail varnish, and jewelry. Rings and earrings that cannot be removed may be covered with adhesive tape. Patients are advised not to eat for six hours before surgery.
- The physician will provide an explanation of the procedure, allowing time for any questions or concerns. Following this discussion, patients will be required to sign a consent form to acknowledge their understanding and agreement to proceed with the surgery.
Procedure
- Patients may experience temporary effects from anesthesia and sedation, which can impair coordination and reasoning skills. Therefore, it is advised to avoid driving, consuming alcohol, making significant decisions, or signing legal documents for 24 hours post-procedure.
- Patients can resume light activities the following day and are encouraged to engage in exercises for the hand on the operated side to help reduce numbness. Supportive, wireless bras are recommended for comfort.
Risks After procedure
- Breast lump removal is generally a safe procedure, with most side effects being mild and temporary.
- Common side effects may include nausea from anesthesia or pain medications, as well as bruising and swelling at the operation site. The skin around the incision may change color, and a lump may appear beneath the scar; both conditions typically resolve over time.
- Potential complications associated with any surgery include unexpected reactions to anesthesia, excessive bleeding, or the formation of a blood clot in a deep vein (deep vein thrombosis).
A specific complication related to breast lump removal is infection, which can generally be treated with antibiotics. Signs of infection may include bleeding, redness, elevated temperature, increased pain, discharge, or hardness in the breast.
References
香港乳癌及乳病治疗中心. 乳癌警号一:乳房硬块要小心-香港乳癌及乳病治疗中心. Available at : https://www.hkbreast.com/breast-lump-the-rail/
Santen, R. J., Mansel, R. (2005). Benign breast disorders. New England Journal of Medicine, 353(3), 275-285.

 3405 8288
3405 8288