Bispectral Index
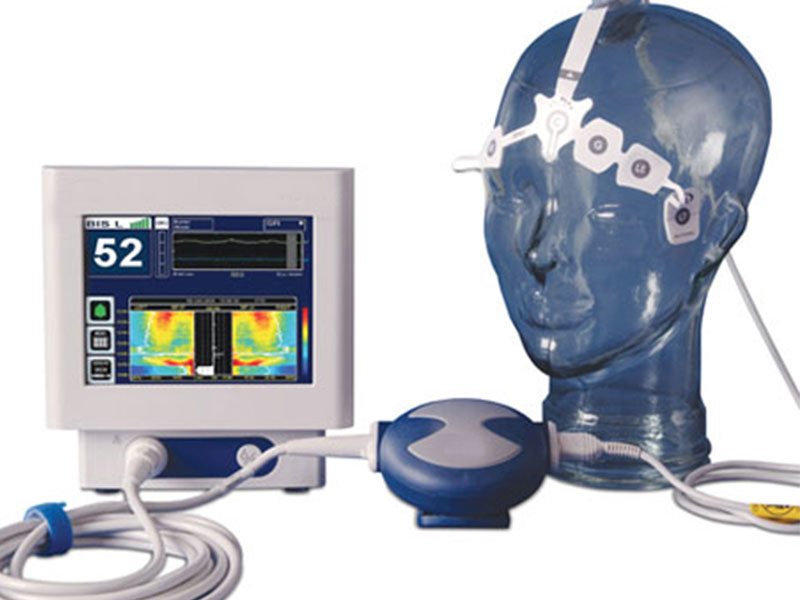
The Specialists introduces BIS Complete 4-Channel Monitoring System (BIS), which is a non-invasive medical system.
To make the system work, doctor will place a sensor on the patient’s forehead to measure the activity of the brain. The EEG data obtained can measure the vital signs and the depth of consciousness of an individual patient under a certain depth of anaesthesia. Hence, it can help improve patient safety by ensuring the correct dose is delivered during the surgery or examination. The BIS scores range between 0 and 100, where 0 means the brain is ‘less active’ and 100 means ‘fully awake’. The conscious patient usually has a high BIS value. BIS values between 40 and 60 reflect adequate effect for general anaesthesia and a score between 60 and 80 after the administration of intravenous anaesthesia. Monitoring the impact of anaesthesia on the brain can improve the safety in surgical procedures, reduce potential side effects of anaesthesia.
The monitoring system is usually applied in the drug-induced sleep endoscopy (DISE). As long as the patient has given the adequate dose of anaesthesia, doctor will place a sensor on the patient’s forehead that connect the monitoring system. The anaesthesia, therefore, will put the patient into the deep sleep during the surgery. When the patient is unconscious, the neurological data can be obtained by the sensor placed on his/her forehead. Other parameters including sleep efficiency, Apnea Hypopnea Index (AHI), blood oxygen levels, breathing rates and patterns, eye movements, sleep stages, unusual movements or behaviours, snoring, and obstruction or narrowing of the upper airway with patients under sedation. The drug-induced sleep endoscopy (DISE) allows to investigate the exact location of the obstruction and to assess the severity of sleep apnea.

 3405 8288
3405 8288