Preauricular Sinus / Fistula
The frontal sinus, also known as the anterior sinus, is a cavity located within the frontal bone of the skull, situated anteriorly to the temporal bone. As part of the paranasal sinus system, which includes the maxillary and sphenoid sinuses, the frontal sinus connects to the nasal cavity through small passages known as ostia.
The primary functions of the frontal sinus include reducing the overall weight of the head, providing sound resonance, and offering protection to the eyes and brain. Additionally, it plays a role in maintaining temperature and humidity balance within the cranial cavity.
When the frontal sinus becomes infected or inflamed, the condition is termed frontal sinusitis. This may be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi and can present symptoms similar to other sinus infections. Congenital abnormalities, such as a fistula connecting the sinus to the skin, may also occur. If the sinus is obstructed, this can lead to infection and the formation of an abscess. A frontal sinusectomy is a surgical procedure designed to remove the frontal sinus and address any scarring resulting from prior infections.
Common Symptoms of Frontal Sinusitis
- Headache: A primary symptom of frontal sinusitis is headache, typically located in the forehead region, varying from mild to moderate intensity.
- Facial Pain: Patients may experience pressure and pain in the face, particularly around the forehead, eyes, and bridge of the nose.
- Nasal Congestion and Discharge: Inflammation of the nasal mucosa can lead to congestion and discharge, which may be thick and yellow or green in color.
- Pressure Sensation in the Head: A sensation of fullness or pressure in the head may occur, often exacerbated by bending forward or tilting the head down.
- Loss of Smell: Some individuals may experience a temporary loss or reduction in their sense of smell during episodes of frontal sinusitis.
- Fever: Severe frontal sinusitis may be accompanied by fever and generalized malaise.
Causes of Frontal Sinusitis
- Upper Respiratory Infections: Frontal sinusitis is frequently caused by viral or bacterial infections, with upper respiratory infections, such as the common cold or influenza, serving as common precursors. These infections can lead to swelling of the nasal mucosa, obstructing the ostia and resulting in infection.
- Nasal Cavity Issues: Structural abnormalities in the nasal cavity, such as a deviated septum, nasal polyps, or congenital malformations, may contribute to the development of frontal sinusitis by impairing normal drainage and ventilation.
- Anatomical Variations: Some individuals may have congenital anatomical variations of the frontal sinus, such as oversized or undersized sinuses, which can increase the risk of infection by obstructing normal drainage.
- Complications from Sinus Surgery: Occasionally, complications from prior sinus surgery can lead to frontal sinusitis due to infections or nasal cavity abnormalities.
- Allergic Reactions: Allergies to specific allergens (such as pollen, dust mites, or pet dander) can cause swelling of the nasal mucosa and increased secretions, potentially leading to frontal sinusitis.
- Immunocompromised States: Individuals with weakened immune systems may be more susceptible to frontal sinusitis due to a reduced ability to combat pathogens effectively.
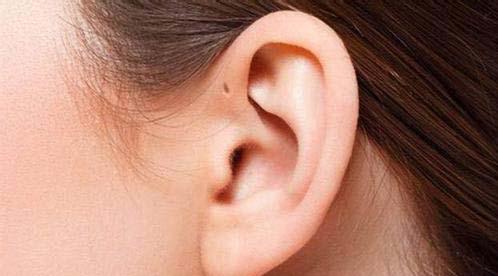
Preauricular Sinuses
Preauricular sinuses are typically located in the anterior area of the ascending limb of the helix. They can occur in various locations, including the superior regions of the auricle, the posterior surface of the cymba concha, and the postauricular area.
Most preauricular sinuses present asymptomatically and do not require treatment. However, when signs of infection occur—such as chronic recurrent discharges, erythematous changes, abscess formation, or local swelling—complete surgical excision of the sinus tracts is recommended.
Indications for Surgical Intervention
- Previous History of Infection: A history of infection in the preauricular sinus may necessitate surgical intervention.
- Symptomatic Relief: Surgical excision may be indicated to alleviate symptoms.
Intended Benefits and Expected Outcomes
-
Prevention of Infection: Surgery aims to prevent recurrent infections.
- Symptomatic Relief: Patients can expect to experience relief from associated symptoms.
The Procedure
- Anesthesia: Local or general anesthesia will be administered.
- Incision: An incision will be made in front of the ear, including the sinus opening and any scar tissue.
- Tissue Removal: Soft tissue along the area, including all tracts, will be excised.
- Haemostasis: Bleeding will be controlled.
- Wound Closure: The incision will be closed appropriately.
- Head Bandage: A head bandage may be applied if necessary.
- Risks and Complications (≥1% Risk)
- Bleeding: There is a risk of postoperative bleeding.
- Wound Infection/Abscess: Infection may occur at the surgical site.
- Wound Breakdown: The surgical wound may not heal properly.
- Poor Wound Healing: Some patients may experience slower healing.
- Scar/Keloid Formation: Scarring may occur as a result of the incision.
- Recurrence: There is a possibility of symptom recurrence.
- Uncommon Risks with Serious Consequences (<1% Risk)
- Damage to Nearby Structures: There is a risk of injury to facial nerves or blood vessels during the procedure.
Before the Procedure
Patients should inform their healthcare provider of any medical conditions (e.g., diabetes mellitus, heart disease, hypertension) and any regular medications, including herbal supplements.
Patients may be instructed to refrain from food and drink as needed prior to the procedure.
After the Procedure
A simple dressing will be applied to the wound. If a head bandage is used, it can typically be removed one or two days postoperatively.
Reference
U.S. National Library of Medicine. MedlinePlus. Frontal Sinus Infection (Frontal Sinusitis) Available at : https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000647.htm

 3405 8288
3405 8288