Uroflowmetry
Symptoms
The urinary infections suffer the old age due to the loosen muscles and ligaments. And the urinary incontinence is the most prevalent urinary problem. More women experience stress incontinence which is related to the poor control of bladder muscle after childbirth.
Other urinary dysfunctions including nocturia, frequent urination, dysuria, difficulty urinating, dribbling urine, and weak urine stream are more common in men than women due to the prostatic hyperplasia. If a male patient experiences difficulty voiding, we suggest the patient to answer the seven questions on The International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS) for a self-assessment.
Urodynamic Testing
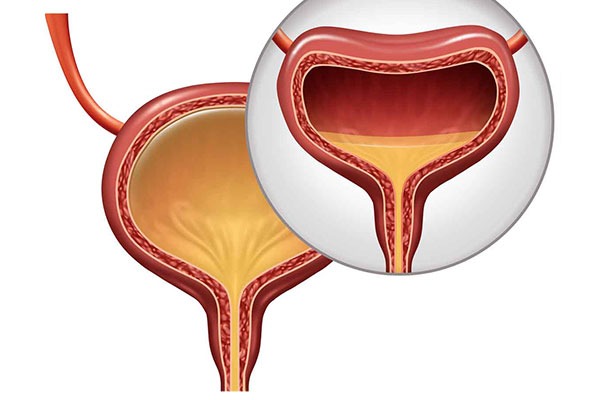
Doctor uses uroflowmetry to find out if the bladder can hold urine and empty steadily and completely. The test contains two parts: the uroflowmetry and the bladder volume measurement. Age, pregnancy, and menstrual cycle do not influence the results.
Fast and Accurate Diagnosis
The radiology nurse guides the patient to complete the test and performs the Bladder Volume Measurement System to evaluate the post-void residual. The results can help the urologist or obstetrician check the function of the bladder and sphincter. It can help determine if the patient is suffered from urinary tract obstruction, and the severity of bladder abnormalities based on the average and maximum rates of the current urine flow.
Examination Process
Patients should hold urine to ensure a full bladder before the test. They urinate as they normally do into a special toilet for the uroflow test. The uroflowmetry (see the image below) is a funnel-shaped instrument that contains automatic measurement parameters to test the speed of urine flow and urination volume. The device will record the average and maximum flow rate, voided volume, voiding time, time to maximum flow and residual urine on a chart. The illustrated report can be issued once the test is finished.
*The above information is for reference only, please consult your doctor for detail.

 3405 8288
3405 8288
