Early detection of liver tumour: Liver specific MRI Contrast Agent
What is a liver tumour?
Liver tumours are tumours or growths on or in the liver. These growths can be benign or malignant (cancerous).
High risk groups and risk factors
- Chronic hepatitis B carrier
- Patient with liver cirrhosis (Common etiologies include chronic alcoholism, hepatitis B, hepatitis C, fatty liver, etc)
Liver tumour examination and accuracy
High risk groups are recommended to have HCC surveillance including liver ultrasound and blood tests for alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) at six-month intervals.
However, ultrasound may miss tumour(s) at an early stage, and may have difficulty in differentiating benign or malignant tumour(s). In case of doubt, contrast-enhanced CT or MRI are the alternative tools that may help.
Abdominal ultrasound:
Ultrasound is employed to scan the structure of the liver to confirm the size and location of the tumour. This test takes several minutes and the patient must stop drinking or eating four hours before the test.
Computed Tomography (CT):
X-ray is used to scan the liver from different angles so as to get a detailed graph, which can display the location and size of the tumour.
Magnetic resonance imaging:
Magnetic field replaced X-ray to construct a cross-section image of the body which includes no risk of exposure to radiation.
Both CT and MRI require contrast injection to enhance the sensitivity and specificity.
Safety ratings
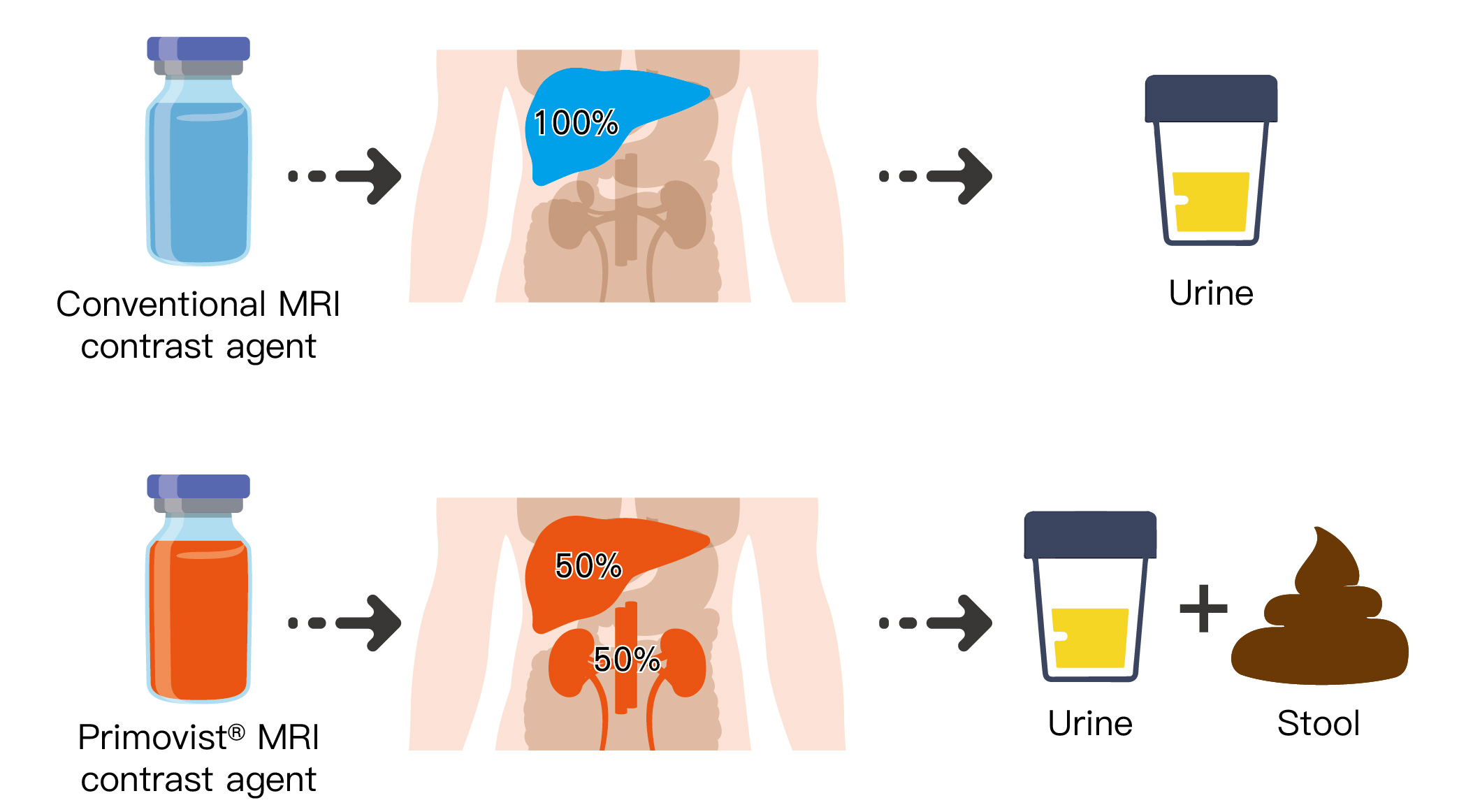
Gadoxetate disodium (also known by the tradenames PrimovistTM and EovistTM) is a novel MRI contrast agent that can be absorbed by the normal liver cell but not tumour cell. Therefore, compared to conventional MRI contrast, it has higher accuracy in diagnosing liver cancer. Besides, primovist also has lower kidney burden compared to conventional MRI contrast. After primovist enters the body, only 50% of it will be excreted in the urine by the kidney, and the other 50% will enter the liver and be excreted in the stool via the bile. Meanwhile, conventional MRI contrast can only be excreted by the kidney alone.
*The above information is for reference only, please consult your doctor for detail.

 3405 8288
3405 8288
