Learn About Breast Cancer

Breast cancer is the most common cancer among females in Hong Kong. It accounted for 26.6% of all new cancers in females diagnosed in Hong Kong in 2016. Rarely, it may also occur in males. In 2016, there were 15 new cases of breast cancer in males.
In 2011, 4108 new cases of female breast cancer were diagnosed and the crude incidence rate was 103.7 per 100,000 female population. The age-standardized incidence rate was 65.9 per 100,000 standard population. From 1983 to 2016, the age-standardized incidence rate had an upward trend.
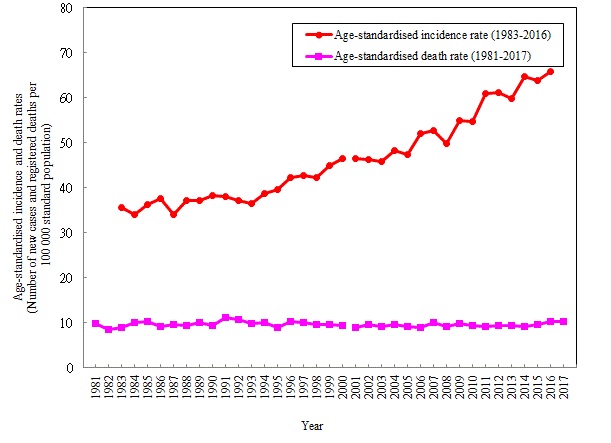
Source: Hong Kong Cancer Registry, Hospital Authority 2017
Symptoms of Breast Cancer
-
Changes in breast size or shape
-
Ridges or pitting on the skin of the breast so that it looks like the skin of an orange
-
A lump or thickening in or near the breast or in the underarm area
-
A nipple turned inward into the breast
-
Spontaneous single-nipple discharge
-
Skin eruption at or near the nipple
Source: Hong Kong Cancer Registry, Hospital Authority 2017
Symptoms of Breast Cancer
-
Changes in breast size or shape
-
Ridges or pitting on the skin of the breast so that it looks like the skin of an orange
-
A lump or thickening in or near the breast or in the underarm area
-
A nipple turned inward into the breast
-
Spontaneous single-nipple discharge
-
Skin eruption at or near the nipple
Relative Risk of Having Cancer > 2-4 times
-
Mother or sister with breast cancer before
-
Giving birth to your first baby after age 35
-
Never having children
-
Being overweight or obese after menopause
-
Having ovarian cancer or endometrial cancer
-
Having radiation exposure to your chest wall
Relative Risk of Having Cancer = 1.1-1.9 times
-
Alcoholism
-
Beginning your period before age 12
-
Beginning your menopause after age 55
Breast Investigation
Triple assessment
-
Clinical examination
-
Imaging
<35 years old:Ultrasound
>35 years old:Mammogram + USG -
Histology examination
Surgery for Breast Cancer
Surgery for breast cancer can be classified into modified radical mastectomy and breast conservation surgery. Modified radical mastectomy excises the whole breast and the lymph tissues at the armpit, while breast conservation surgery must be accompanied with post-surgical radiation therapy.
1. Lumpectomy
This is the removal of the breast lump together with some surrounding tissue. A lumpectomy is now possible for many women. It removes the least amount of breast tissue, but leaves a small scar and sometimes a small dent in the breast. For most women, the appearance of the breast after lumpectomy is good.
2. Segmentectomy (wide local excision)
This is similar to a lumpectomy but as it involves removing more breast tissue, then it may be more noticeable, particular in women have small breast. In women with large breasts it is usually less noticeable.
3. Mastectomy
A mastectomy removes the whole breast, including the skin and the nipple. Usually the lymph nodes in the armpit are also removed during the operation. This is called axillary clearance or dissection. After mastectomy, most women have a horizontal scar across their chest. Other side effects include: infection, a reduced sensitivity due to nerve damage and swelling of the arm (lymphoedema). Improvements in surgical techniques have made these side effects less common. For many women the breast can be reconstructed after the surgery.
4. Lymph gland removal
With any of these operations, the surgeon will usually remove lymph glands from under your arm. This is done to check whether any cancer cells have spread from the breast and helps doctors decide whether other treatment is needed. Some doctors remove all the armpit lymph glands, while others take just a few lymph glands as a representative sample.
Comparison Between Breast Conservation Surgery and Mastectomy
|
Lumpectomy: |
Mastectomy: |
|
Retain the breast (Excise the tumour plus a rim of normal breast tissue) |
Excision of the whole breast |
|
Smaller wound |
Larger wound |
|
Shorter time of hospitalization |
Longer time of hospitalizatio |
|
5-6 weeks of radiotherapy is a must |
|
* There are not much differences in the recurrence and survival rate between the two kinds of surgery.
Conservation Surgery is not Suitable for Persons who:
-
Have a lump larger than 5cm (A comparison between the size of the lump and the breast is a must)
-
Cannot undergo radiotherapy (e.g. those who are pregnant, used to underwent radiotherapy at the same site or suffer from connective tissue diseases)
-
Have multiple sites of cancer at one breast
-
Depends on his/her choice
Complications/Side Effects of Surgery for Breast Cancer
The complications of surgery for breast cancer includes numbness of skin at the breast and armpit, lymph edema, pain, infection, hematoma and cleavage.
Follow-up and Further Investigations
Regular follow-up and investigation is needed to look for recurrence.
Catch Breast Cancer by Early Examination
-
Females aged above 20 should perform a breast self-examination (BSE) each month after the end of their menses to see if there are any changes such as lumps and pitting at the breast.
-
Perform clinical examination regularly.
Breast Screening*
|
Age |
BSE |
Clinical Examination |
Mammogram |
|
20-34 |
Every Month |
Every 3 years |
/ |
|
35-39 |
Every Month |
Every 2-3 years |
First time |
|
40-49 |
Every Month |
Every 2 years |
Every 2 years |
|
50+ |
Every Month |
Every 2 years |
Every 2 years |
※Please pay attention to the appearance, feeling and changes of your breasts when you perform BSE. Consult your doctor once any abnormality is found.
*The information is provided by Hong Kong Cancer Registry http://www3.ha.org.hk/cancereg/
How is Breast Cancer Staged?
|
I |
The tumor is 2 cm or less across and has not spread to lymph nodes or distant sites. |
|
II |
The tumor is 2 to 5 cm large and may or may not have spread to lymph nodes. The cancer has not spread to distant sites. |
|
III |
The tumor is larger than 5cm across, and has spread to lymph nodes. The cancer has not spread to distant sites. |
|
IV |
Tumors in the breast can be any size and they may have spread to lymph nodes and nearby organs. |
*The above information is for reference only, please consult your doctor for detail.

 3405 8288
3405 8288
